Given an integer n, return the number of strings of length n that consist only of vowels (a, e, i, o, u) and are lexicographically sorted.
A string s is lexicographically sorted if for all valid i, s[i] is the same as or comes before s[i+1] in the alphabet.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1
Output: 5
Explanation: The 5 sorted strings that consist of vowels only are [“a”,”e”,”i”,”o”,”u”].
Example 2:
Input: n = 2
Output: 15
Explanation: The 15 sorted strings that consist of vowels only are
[“aa”,”ae”,”ai”,”ao”,”au”,”ee”,”ei”,”eo”,”eu”,”ii”,”io”,”iu”,”oo”,”ou”,”uu”].
Note that “ea” is not a valid string since ‘e’ comes after ‘a’ in the alphabet.
Flow Diagram: –
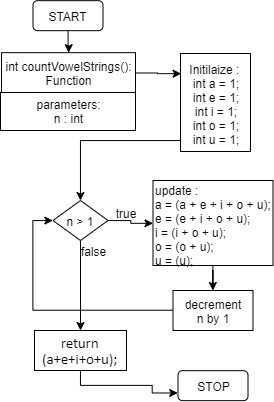
Solution: –
class Solution {
public int countVowelStrings(int n) {
int a = 1, e = 1, i = 1, o = 1, u = 1;
while(n > 1) {
// add new char before prev string
a = (a + e + i + o + u); // a, e, i, o, u -> aa, ae, ai, ao, au
e = (e + i + o + u); // e, i, o, u -> ee, ei, eo, eu
i = (i + o + u); // i, o, u -> ii, io, iu
o = (o + u); // o, u -> oo, ou
u = (u);; // u -> uu
n--;
}
return a + e + i + o + u;
}
}